Your network is a hyper-logical pathway for your devices to connect to each other. However, if you don’t explicitly and properly configure all the parts, traffic can easily be lost because your networking devices won’t know what to do with it. To add on top of that, the larger and more complex it gets, the more unwieldy it can become to manage and troubleshoot.
Here are a few areas we frequently find issues with when troubleshooting a network:
VLANs Between Switches are Misconfigured
When you’re trying to push traffic to and from a switch, it must be on the same VLAN as your host (the device in question trying to connect on the network). If the IP address does not match the same VLAN name, the switch will put it into an incorrect VLAN. In other words, make sure your VLANs match up. While this can occur for users, this is a more common problem with servers.
The same goes between switches as well. The VLAN tags must match up on your trunk ports or your traffic will get dropped by the switch.
Missing or Misconfigured DHCP Scopes
Your DHCP scope in your DHCP server assigns IP addresses, your DNS server, your subnet mask and your default gateway. It may assign other things, but these are the most common. If any of it is misconfigured, you’re likely to have communication issues. If DNS isn’t properly set up, you will not be able to access anything with names, i.e. Google or the name of your file share. Issues with subnet masks can cause issues talking to neighboring VLANs, since the computer is functioning off of knowing what is local to it and what is not, and the subnet mask defines that. Issues with your default gateway essentially stop any communications to any other networks, including the internet, so you’ll know pretty quickly if that’s your issue.
IP Helpers Not Connected to DHCP
Your switch has this function for each VLAN that points DHCP requests to the DHCP server. So, if you’re having trouble getting IP addresses assigned, it could be with your IP Helpers (if not a missing DHCP scope). Your IP Helper must be configured to point to the DHCP server to forward the request for an IP address and then relays the response back to the host.
Basic Troubleshooting Steps
In the event that you’re experiencing some form of communication issues on your network, like the inability to connect to anything or everything, here are certain steps you can take to try and isolate the root cause of the issue.
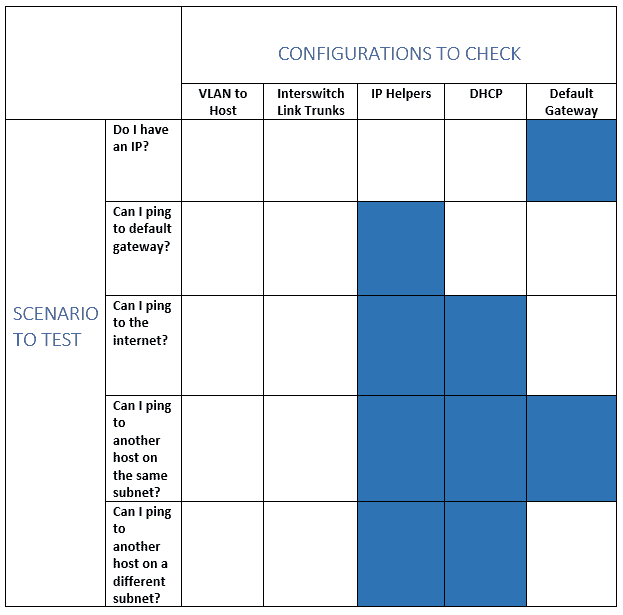
We’ve made them into a chart of scenarios and spot checks to follow when troubleshooting some of these common issues. The blacked out sections don’t apply to that particular scenario, but fill in a check box in the empty ones once you’ve verified the config is good in each of the scenarios listed below in order to more easily pinpoint where your problem is originating from.