What is it?
In the simplest of terms, the maximum transit unit, or MTU, is the set of data in bytes that can travel in a packet. Varying factors, like environment, hardware, software, and ISP, can determine the packet size. Because of the many factors, there can be multiple MTU size requirements within your environment. By default, MTU is set to 1500 bytes.
Why you might need to change it
Having the incorrect MTU set can cause packet fragmentation and hinder the transfer of data. If you’ve noticed a slow connection between your firewall and server or users have complained about internet speed, you may want to test your MTU.
How to find it
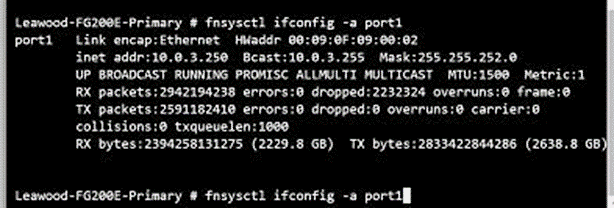
To determine your MTU, run an Ifconfig from the Fortinet FortiGate by running this command: fnsysctl ifconfig -a port1. Port1 is the port I needed to get the info for, you can change this accordingly. Check out the screenshot below. If the MTU has never been altered, it should be set to the default at 1500.
In this screenshot you can also see that this command displays MAC and dropped packets.
How to change it
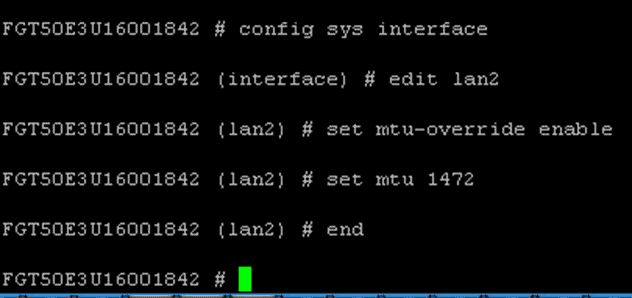
Now that you know where to find the MTU size, you might want to change it to keep packets from being fragmented. Start with this command:
config system interface
edit <interface_name>
set mtu-override enable
set mtu <byte_size>
end
It should look a little like this:
That’s it! Changing the MTU is a simple and easy way to get your network running smoothly and more efficiently.