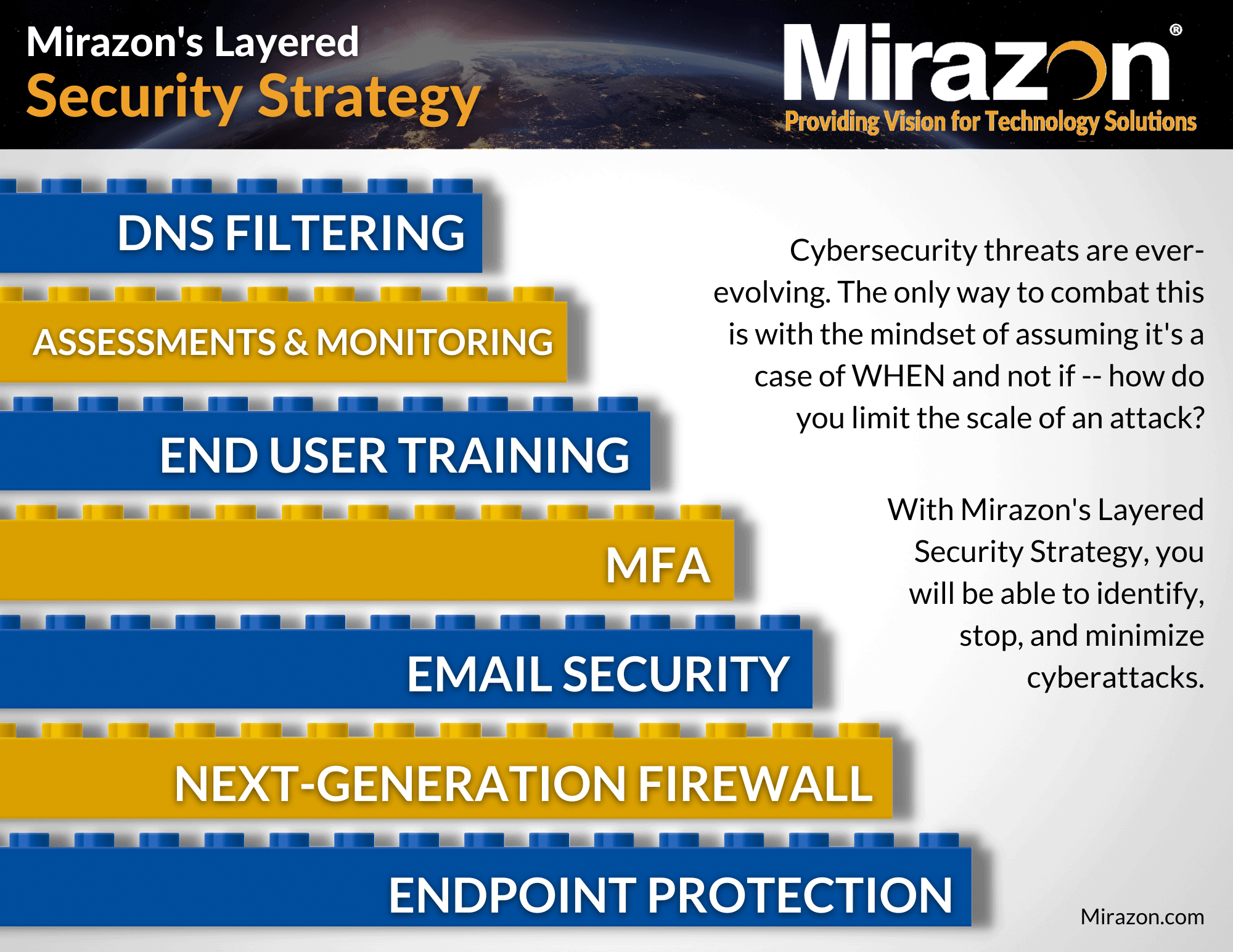
In our previous Defense In Depth blog series, we’ve delved into the realms of Endpoint Protection, Next-Generation Firewalls (NGFWs), and the intricacies of Email Security. Now, we’re about to unlock a new level of security as we explore Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) – the fourth layer of our Layered Security Strategy, to be exact.
In today’s digital world, there is an increased need for security measures that can prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data. That being said, username and password combinations just won’t cut it anymore. This is where MFA comes in.
Implementing MFA in your security strategy can provide an additional layer of protection, as it requires users to provide more than one form of identification before granting access (we’ll talk more about this later).
Here, we’ll discuss MFA’s relation to having a robust layered security strategy, its importance to business and IT infrastructure security, commonly overlooked factors, and best practices.
MFA & Importance To Business And IT Infrastructure Security
In today’s digital age, the very fabric of business operations has shifted towards the online realm, as organizations increasingly rely on digital infrastructure to manage their processes, communication, and data. With this digital transformation, however, comes a parallel rise in cybersecurity threats, making the inclusion of Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) an essential component of any comprehensive security strategy.
By requiring users to provide multiple forms of verification before gaining access to critical systems and data, MFA greatly bolsters security – and the importance of MFA to your business and IT infrastructure security cannot be overstated. Here’s why:
Protection Against Unauthorized Access:
MFA requires users to provide multiple factors of identity verification to gain access to their accounts – typically something they know (such as a password), something they have (such as a one-time password from a mobile device or a physical token), or something they are (such as a fingerprint or facial recognition).
By combining these different factors, MFA significantly enhances the security of user and business accounts and helps prevent unauthorized access – because even if one factor is compromised, the attacker would still need the additional factor(s) to gain entry. Furthermore, MFA can alert IT managers when there is an attempted breach, providing them with an opportunity to take necessary actions. This makes it significantly more challenging for hackers to compromise your systems.
Data Security
Your organization’s data is its lifeblood, and its protection is paramount. A breach in your IT infrastructure could lead to the loss of sensitive information, intellectual property, and customer data. MFA helps safeguard this data, reducing the risk of unauthorized access and data exfiltration.
Reputation Management
The consequences of a security breach extend far beyond the immediate financial impact. Your reputation is at stake, and a security incident can erode the trust your customers, partners, and stakeholders place in your organization. MFA demonstrates your commitment to security, reassuring those you do business with that their information is in safe hands. It also helps to create a culture of security within your organization.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
In an increasingly regulated environment, failing to adequately secure your IT infrastructure can lead to legal repercussions. Depending on your industry and geographic location, non-compliance with data protection and privacy regulations can result in significant fines and legal actions. MFA is often a requirement or strongly recommended by various regulatory bodies. And let’s not forget, if you’re looking into obtaining cybersecurity insurance, or already have it, MFA is a baseline requirement. If you aren’t implementing it, you are not meeting compliance standards.
Take our Cybersecurity Insurance Posture Assessment!
Business Continuity
A security breach can disrupt your operations, leading to downtime, financial losses, and operational chaos. MFA helps ensure the continuity of your business by reducing the likelihood of breaches and their associated disruptions.
In summary, MFA is not just a security feature; it’s an insurance policy for your business and IT infrastructure – a proactive step toward ensuring the resilience and security of your digital operations.
Commonly Overlooked Factors Of MFA
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is a powerful tool in the arsenal of cybersecurity, but its effective implementation requires careful consideration of various factors. In the pursuit of enhanced security, many IT managers inadvertently overlook aspects that can impact user experience and the overall success of MFA deployment.
Let’s delve into these commonly overlooked factors and explore strategies to address them:
User Friendliness
One of the common pitfalls in MFA implementation is neglecting the importance of user-friendliness. Introducing an MFA solution that is complex, cumbersome, or confusing can lead to resistance among users. In such cases, employees might circumvent or bypass MFA, inadvertently weakening security. To address this challenge, IT managers should opt for user-friendly MFA solutions that offer a seamless and intuitive experience.
Strategy: Providing adequate training and support for users is paramount. IT managers should ensure that employees understand the purpose and benefits of MFA. Training can empower users to navigate the MFA process confidently, reducing frustration and resistance.
Implementation Strategy
A lack of a well-defined implementation strategy can lead to confusion among users. IT managers should have a clear plan in place and communicate it effectively. Informing users about the upcoming changes, the reasons behind them, and the steps they need to follow can minimize frustration and anxiety during the opt-in process.
Strategy: Before deploying MFA across the entire organization, consider running pilot programs or testing phases. This allows IT managers to identify and resolve any issues or concerns in a controlled environment, ensuring a smoother rollout.
Recovery & Backup Procedures
MFA can be a double-edged sword. While it enhances security, it can also lock users out if they lose their second factor, forget their credentials, or face technical issues. Implementing a robust account recovery process is essential. This might include security questions, backup codes, or alternative authentication methods to ensure users can regain access to their accounts.
Strategy: It’s crucial to have redundancy and backup systems in place, particularly for critical services. In the event of MFA system failures or outages, having alternative methods for accessing systems can prevent significant disruptions.
Scalability
Organizations evolve, and their needs change over time. A commonly overlooked factor is ensuring that the chosen MFA solution is scalable.
Strategy: Ensure your chosen MFA solution is able to accommodate the growth of users and systems without causing bottlenecks or compromising security.
Integration with Existing Systems
Integration of MFA with existing systems, applications, and services can be challenging but is crucial for a cohesive security strategy. Not to mention, with proper integration, comes ease of use for your employees.
Strategy: IT managers should consider the compatibility and ease of integration of MFA solutions with the organization’s current technology stack.
Compliance & Regulation
Different industries and regions have specific data protection and privacy regulations that may impact MFA requirements. It’s critical to be aware of what those requirements are, especially for cybersecurity insurance.
Strategy: IT managers should be aware of these and ensure that their MFA implementation aligns with applicable compliance standards.
MFA is a potent defense against cybersecurity threats, but its effectiveness hinges on careful consideration of these often overlooked factors. IT managers must prioritize user-friendliness, a well-planned implementation strategy, recovery procedures, scalability, integration, and compliance. By addressing these challenges, organizations can harness the full potential of MFA while maintaining a secure and efficient digital environment while also protecting against an increasingly prevalent issue known as MFA fatigue (read more about this here).
MFA Best Practices
When implementing MFA, it’s essential to follow best practices to ensure its efficacy. So, let’s talk about some of these best practices and what you need to keep in mind for your organization and IT infrastructure.
Layered Approach
Implement MFA at multiple levels within your organization, especially for critical systems and sensitive data. By layering MFA throughout your infrastructure, you create multiple lines of defense against potential breaches.
MFA Options
Offer diverse authentication methods to users. While traditional methods like SMS codes or email notifications are widely used, consider more secure options like TOTP or hardware tokens.
Risk-Based Authentication
Integrate risk-based authentication into your MFA strategy. This approach evaluates the risk associated with a login attempt based on factors such as location, device, and user behavior.
User Education
Provide clear and concise information to users about MFA and its benefits. Educate them on how to set up and use MFA, and stress the importance of safeguarding their authentication methods.
MFA for Third-Party Services
Extend MFA to third-party applications and services that your organization uses. Even if you’re not in control of the authentication process, ensure that the services you rely on support MFA.
Monitoring & Alerts
Set up monitoring and alert systems to detect unusual MFA activities, such as multiple failed attempts or successful logins from unfamiliar locations. Promptly address any anomalies to prevent security breaches.
Regular Audits
Conduct regular security audits to review the effectiveness of your MFA implementation. Assess which users have MFA enabled, identify any inactive users, and ensure compliance with your organization’s security policies.
Adaptive MFA
Consider using adaptive MFA solutions that can adjust authentication requirements based on contextual factors (ex., unusual user login locations outside the norm, prompting for additional authentication).
SSO Integration
Integrate MFA with your Single Sign-On solution. This streamlines the authentication process for users while maintaining robust security for all the applications and services connected to the SSO.
Account Recovery Protocols
Develop and communicate clear procedures for account recovery in case users lose access to their primary authentication method. This can include backup codes, security questions, or alternative methods of verification.
Compliance & Regulations
Ensure that your MFA implementation aligns with relevant industry-specific regulations and data protection laws. This helps you remain compliant and avoids legal issues.
Incident Response Plan
Develop a comprehensive incident response plan that includes protocols for handling MFA-related security incidents. Knowing how to respond in the event of an MFA breach is as important as prevention.
Regular Training & Awareness
Keep your users informed and engaged with ongoing training and awareness programs. Cybersecurity threats evolve, and so should your users’ understanding of MFA and other security practices.
By following these MFA best practices, you can fortify your organization’s security posture, protect sensitive data, and empower your users to navigate the digital landscape with confidence. MFA is not just a security feature; it’s a critical component of a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy.
Conclusion
Multi-factor authentication is an essential component of a robust security strategy. With the increasing number of data breaches, businesses must prioritize implementing MFA to protect their IT infrastructure and sensitive data. By following best practices and addressing commonly overlooked factors, IT managers can ensure successful implementation and reap the benefits of MFA, such as increased security and compliance with industry regulations. Don’t let your business become a victim of a cyberattack – contact us and implement MFA today.
Stay tuned for our next Defense In Depth blog, which will cover End-User Training and SAT.
If you’d like to learn more about Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and how you can use it to better protect your business, please contact us by calling (502) 240-0404 or emailing info@mirazon.com.